If you are a salaried individual in a private or public firm, you must make yourself familiar with your basic salary structure. Your salary structure is divided into lot of components like travel, HRA, food, etc. Some of these components are taxable while some are tax exempt. You must be familiar about each of the components of your salary so that you know your tax obligation.
There is also a lot of difference between your CTC (Cost to company) and the take home salary that you get. If you have a clear understanding of your basic salary structure, it is easier to comprehend your in-hand salary. So, the next time if your CTC is great but your take home is less, you should negotiate well for your own benefit.
Let us first begin by first understanding the basic components of your salary which is common to most of the salaried group.
This is how a basic salary structure looks:
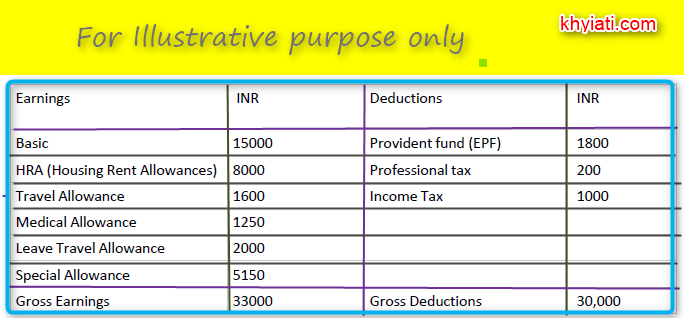
Note: The figures above are just for illustration purposes. They might not reflect the actual calculation.
For an employer, that provides numerous components to your basic salary structure, in addition to the above, your earnings might also have any of these:
Earnings side;
a. Statuary Bonus
b. Telephone Allowance
c. Internet Allowance
d. Food Allowance
e. Medical Reimbursement
f. Shift Allowance
g. Performance Pay
h. Arrears and Leave Encashment
On the deductions side, you may have:
a. Insurance
b. Recovery for Salary Advance
c. Other Deductions
We will first delve deeper into the basic salary structure and then we will briefly about other components.
Basic Salary Structure
In your basic salary structure, for earnings you will always have:
- Basic
- HRA
- Travel Allowance/Conveyance
- Medical Allowance
- Special Allowance
For deductions, you will always have:
- Professional Tax
- Provident Fund
- Income Tax Deductions (if you fall in the taxable slab)
We will try to understand what each of them mean.
First let us begin with the earnings side:
Basic:
This is the basic salary which you would be getting from your employer. It is a fixed component in your basic salary structure. Overtime, bonuses, benefits or any other kind of components are not included. It forms the major part of your salary. High basic salary is liable to more tax than a low basic salary. Usually, the basic salary should not be more than 40% of your CTC (Cost to Company). Many other components which forms a part of your salary is based on the amount of your basic salary. For example, your pf contribution is a percentage, as deduced from your basic salary.
Housing Rent Allowance:
This is the allowance that you get from your employer irrespective of whether you own your house or live in a rented flat. However, if you live in a rented flat, you are exempt from paying any taxes on it. On the other hand, if you have your own house, this will be taxable for you.
There is a limit to the amount of HRA that are tax deductible. It can be fully or partially tax exempt depending on your basic salary. Also, if your yearly rent is exceeding 1,00,000 INR, then you need to produce the PAN card of your owner.
For more details, read the detailed article on how to calculate HRA.
Medical Allowance:
The Income tax department allows a medical reimbursement of 15,000 INR per year. So, this will come under your medical allowance. Ideally, most of the organization will provide this amount to their employees. It is exempt from tax if you can show bills worth 15,000 INR on your medical. This could be the medicine that you have purchased for yourself or your dependents, medical treatments, doctor consultation, etc. Only the bills of the current financial year are considered under exemption. It typically starts from April and end on March of next year.
Do not confuse this with medical insurance. Medical insure requires that you are admitted to the hospital for atleast 24 hours and then only you can reimburse the amount. However, medical allowance refers to those expenses of yours which does not require any hospitalization.
If your organization is providing medical allowance for more than 15,000 INR, then the amount exceeding 15,000 INR would be taxable. Also, if you are not able to show the medical expenses of 15,000 INR, then only that amount will be exempted which has been spent on medical needs.
Travel Allowance:
Travel Allowance is the allowance that you get from your employer for day to day travel. To reach office from your place of stay, you would incur some expenses. This is given by your employer in the form of conveyance or travel allowance. It is 1600 INR per month or 19,200 INR per annum. This amount is exempted from any taxes. If your employer is providing you the transport, then you would not get this allowance.
Food allowance:
Ideally, your employer can give you food allowance of not more than 50 INR per day. This makes it (26*2*50) per month i.e. 2600 INR per month. Beyond this amount, it is taxable. However, if 2600 INR is paid to you in cash, then also it is taxable. But if you opt for food coupons or meal card, then it is fully exempt from taxation.
Leave Travel Allowance:
Leave Travelling allowance or LTA is the allowance that you are paid by your employer for the long trips that you take within India. It is not applicable for international trip. LTA can be availed only twice in a block of four years. The current block of year is 2014-2017. However, it can be carried forward to the next. Only the fare expenses can be included in this. You can also include the fare expenses of your Family but not relatives. No proof is required from the IT department for this allowance. Nonetheless, your employer may ask you to furnish proof for your travel expenses.
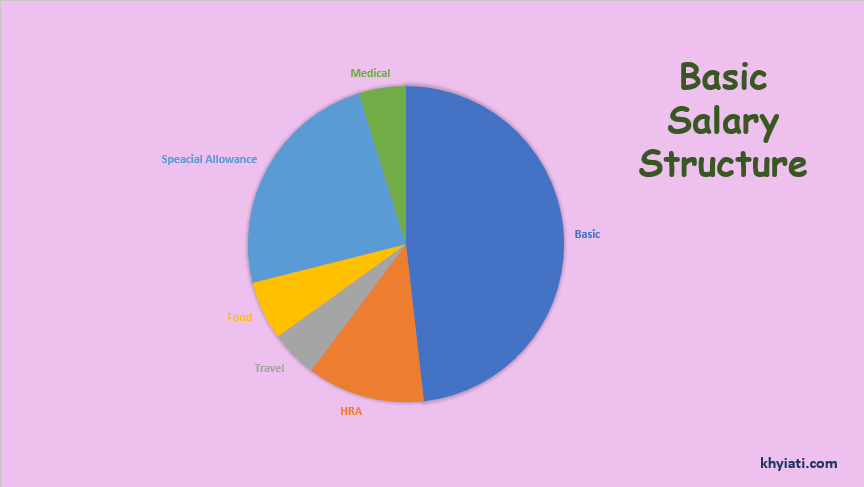
Special Allowance:
After adding all the components described above, the rest of the salary is reflected in the special allowance. This component is fully taxable and there is no exemption on it, whatsoever.
Other allowances:
Statuary Bonus:
Employers might give you bonus depending on the profit earned per year. This component is not mandatory and depends on your employer’s policy. Bonus is usually given once or twice in a year. It also depends on the performance of an employee during a year. Usually, bonus is given along with your performance appraisal.
Telephone allowance:
If you are given telephone allowances every month, then it is taxable. However, if you are reimbursing the amount by producing original bills, then it is fully exempt. For an exemption, you must have a post-paid connection. Prepaid connections are not allowed. How you are taxed will depend upon your company policy.
Internet allowance:
If you are given internet allowances every month, then it is taxable. However, if you are reimbursing the amount by producing original bills, then it is fully exempt. But the final discretion of taxation will depend upon your employer.
Medical Reimbursement:
Generally, medical reimbursements are applicable only if you or your dependents are hospitalized for at least 24 hours for some medical treatments. This might be fully or partially reimbursed based on the medical treatment. Whether this will be taxable or not will depend on your employer.
Shift Allowance:
If your employer pays you for working extra hours or working in a different shift, then you are entitled for this allowance. This is taxable.
Performance Pay:
If there is any amount to be paid to you as per your performance, then you would get an amount as performance pay. This usually comes into picture if there is any variable pay attached to your salary structure. This is taxable.
Arrears and Leave Encashment:
If you have not used your leave(s) for a financial year, your employer might reimburse the amount at the end of the financial year. However, most employers just pay the basic of your salary. Some employers might allow carry forward of the leaves. Some might consider it as lapsed. This will all depend on your company policy. This is considered as leave encashment.
However, if there has been any delay in the payments of your salary or rather increased salary, then this amount is credited as arrear. This usually happens when your hiked salary is delayed for some reason.
Any amount that is credited in this section is taxable.
Coming to the deductions:
Professional Tax:
It is a tax that is levied by the state government to all the people who are earning. This amount is usually 200 INR or so irrespective of whether you are taxable or not. Professional tax however, varies form one state to the other.
Employee Provident Fund:
If your employer is providing you with EPF facility, you may be allowed to contribute 12% of your basic salary or 1800 INR. This is deducted each month from your salary. If your employer is also contributing towards your EPF, then this will be reflected in your CTC.
Note: Always remember that the deductions for EPF on your CTC is reflecting the one that will be paid by the employers, and not yours. Your contribution of EPF will happen separately. It will be deducted each month.
Income Tax Deductions (if you fall in the taxable slab):
There are various taxable slabs according to which you are taxed a certain amount. In a gist, if your earnings are less than 2,50,000 INR per annum, you are not liable to pay any taxes. Above this amount, your taxable amount will vary as per your salary structure.
Insurance:
Some employers provide insurance by charging a certain amount from the employee’s CTC. This may vary as per your salary structure. If so, it will be reflected in your CTC. However, some employers may provide you insurance benefits outside your CTC. This will be as per your company policy.
Recovery for Salary Advance:
If have taken loan against your CTC from your employer, then you will see this component. The loan amount is usually 10% or 20 % of your CTC. The employer will reimburse the amount to you in advance and then deduct certain amount from your salary every month. This component will also come into picture if your company policy provides so. Usually, employers will make you sign a bond that you stay with the organization till you pay all the advances.
Other Deductions:
There might be other deductions and all of this might grossly come under other deductions. It might be a donation, welfare funds, contribution towards anything, etc.
I hope this lengthy article somewhat clarifies the basic salary structure. We have written separate articles on each and every component of salary structure in much greater details. Do go through them.

Leave a Reply